Imre Hegedus
Research Institue of Biomolecular and Process Engineering, University of Pannonia, Veszprem, Hungary
Title: Optimization of synthesis methodology for α-chymotrypsin enzyme nanoparticles
Biography
Biography: Imre Hegedus
Abstract
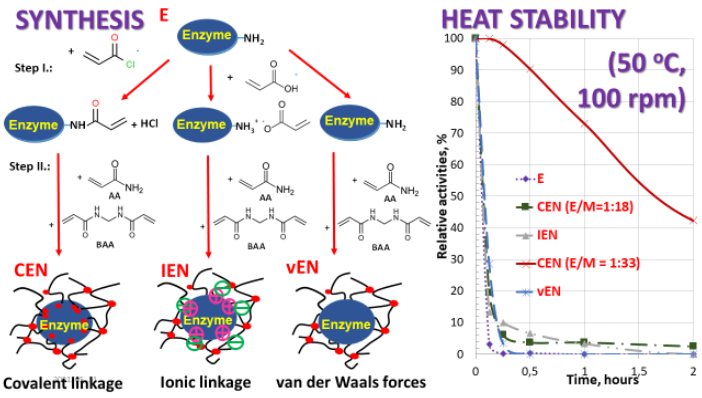
Statement of the Problem: Enzyme nanoparticles represent a new class of nanomaterials with acceptable biocatalytic activity and very long life-time. Polymerization initiated from the modified surface of the enzyme (see Image, Step I and II) leads to enzyme molecules covered with a polymer layer. These may have at least one order of magnitude longer lifetime than that of free enzymes. However, their bio-catalytic activity is at least about 50% less than that of free enzymes. It is not clear how the size of the polymer layer and the strength of enzymepolymer bond influence the stability of enzyme nanoparticles.
Methodology & Theoretical Orientation: α-Chymotrypsin enzyme (bovine) was used for the synthesis. Enzyme nanoparticles containing covalent bond (CEN), ionic binding (IEN) and connected with van der Waals forces (vEN) between enzyme molecule and polymer layer are synthesized (see image: SYNTHESIS) and their bio-catalytic activity was investigated at 50 oC (optimal temperature 37 oC). All products were stirred with 100 rpm and samples were withdrawn from time to time for standard activity measurements (ref. 1.)
Findings: The results show that there is a significant difference between the stability of enzyme nanoparticles synthesized by different methods. CEN has the longest lifetime (about 1.7 hour even at 50 oC), when the enzyme:monomer ratio (E/M) during the synthesis is 1:33, but it is the shortest when E/M = 1:18. There is no significant difference between half-lives of E, IEN, vEN and CEN when E/M=1:18 (value is about 0.1 h in all of these cases) (See image: HEAT STABILITY).
Conclusion & Significance: It seems that the minimal amount of E/M for synthesis of efficient product is about 1:30. This ratio results significant enhance of its half-lifetime (ca. 17 times). Enzymes stabilized by polymer layer with ionic and van der Waals interactions could not result in significant stabilization.